Trimester 2- Winter, 2015/2016
Welcome to the world!
Global Studies B
Activity: Those who didn’t turn in the assignment on the Nazi Program should do so immediately for full credit. It is worth 5 pts
Next, we look at the cycles of inflation in Germany in the early 1920s that helped lead to Hitler’s rise to power in Germany. Students do guided note-taking on the form linked HERE
Interwar Years
T/O (Topic/Objective): Hitler's rise to power
EQ (Essential Question): Why was Hitler successful in leading Germany into a authoritarian, fascist regime that carried out a policy of genocide?
Cycles of inflation in Germany post-WWI . . .
1) Germany has huge war-related expenses after WWI
2) Government spends more than it takes in
3) Germany prints more money
4) Value of money goes down
5) Prices go up
6) Government prints more money
7) Cycle continues
8) Economy is in danger of collapsing
German govt. was printing 400 quadrillion marks/day by 1923 - 400,000,000,000,000,000!!
Hitler's Rise to Power
WWI - 2 Iron Crosses for bravery
1919 - Joined Nazis in Munich, Germany
1923 - Failed attempt to seize power . . .
Nine months in prison - Wrote Mein Kampf . . .
. . . 'Master race' theory
. . . Jews, Gypsies (Roma), Slavs were inferior
. . . Versailles Treaty was an outrage
. . . Lebensram theory revived
1924 - Revived Nazi Party
1930 - Great Depression; Germany economy collapsed
Hitler's Rise to Power
1932 - Nazis became largest party in Germany
1933 - Hitler named chancellor
1933 - Start of the Nuremburg laws
1934 - SS arrests & kills many of Hitler's foes
1936 - Dramatic drop in unemployment followed infrastructure build-up
1938 - Kristallnacht
The Rise of Japanese Militarism
1922 - Agrees to leave China alone
1928 - Renounces war in Kellogg-Briand Treaty
1929 - Onset of Great Depression . . . Government is blamed
1930 - Militarists take control; want to expand to help economy
1931 - Invades Manchuria (NE China)
1933 - Withdraws from League of Nations
1937 - Invasion of greater China . . . 'Rape of Nanjing'
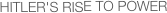
January 11, 2016
Unit 2: Interwar Years & WWII
•We see how the loose ends that weren’t tied up in the aftermath of WWI lead to the rise of fascism in Europe while, at the same time, a militaristic regime takes hold in Japan.
•The Study Guide and Reading Schedule for this unit are linked HERE
•Vocabulary Development forms are available HERE
•The course syllabus for this trimester is linked HERE









